The Science And Mechanics Behind The Sound
Have you ever wondered what makes music sound different? Or why some sounds have a greater impact on us than others? In this blog post, we will explore the science and mechanics behind sound and how it affects us. We will start by defining sound waves and how they interact with our ears. Then, we will look at how certain frequencies, instruments, and tones can impact us. Finally, we will examine the impact of sound on us as humans. By the end of this blog post, you will have a deep understanding of the science and mechanics that make up sound.
Visit this Website: Washington Post
Sound Waves Explained
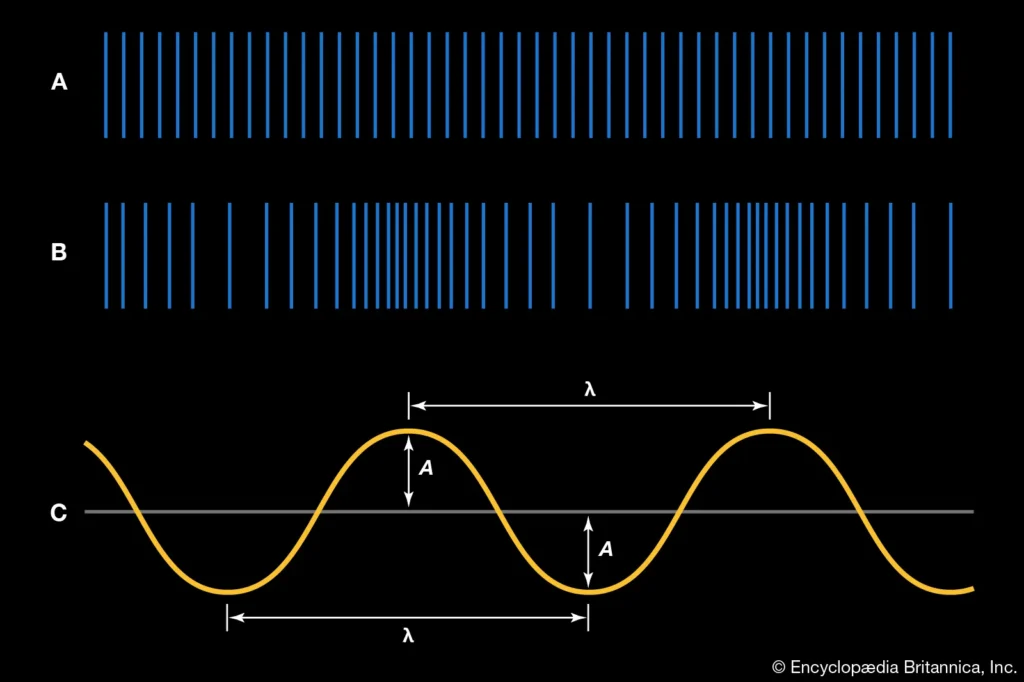
Sound waves are all around us – they’re what we hear when we listen to music, talk on the phone, or watch TV. Sound waves travel through the air and interact with other objects, which is why they can be heard so clearly. Sound waves are made up of tiny particles called sound waves and they can be divided into two main types: longitudinal and transverse.
Longitudinal sound waves move back and forth along a line, while transverse sound waves move across a surface at right angles to the direction of the wave. This is why you often hear sounds coming from all directions at once – because different parts of your ear are hearing different frequencies of sound!
Different sounds are made using different types of sound waves. For example, high-pitched sounds (like those made by babies) are produced using longitudinal soundwaves, while deep bass sounds (like those in thunder or submarines) are created with transverse soundwaves. Think about it this way: if you put your hand in a bowl of water and make a slapping noise with your palm, you’re making a transverse wave – it’s just not very loud!
Sound travels fastest when it’s in direct contact with something else (like air), but it’ll still be heard by our ears if it’s nearby enough. This is why you can’t hear things perfectly from far away – our ears have to focus on picking up the signal! And finally, as we mentioned earlier, noise pollution refers to unwanted noise that’s above acceptable levels – like street noise or industrial machinery that’s working late into the night. It has negative impacts on both our physical and mental health, leading to decreased productivity and increased stress levels. Here are some ways that you can reduce or prevent noise pollution in your life:
– Use earplugs when listening to music or watching TV at night
– Avoid talking on the phone outside during busy hours
– Keep your windows closed during noisy days.
How Sound Travels And Is Processed By The Brain
Sound travels through the air and is processed by our brain in order to create a perception of sound. In this blog, we will explore the various properties of sound and how they affect our brains. We will also look at how different frequencies produce different types of sounds, and how our ears and brain process these sounds. Finally, we will discuss some of the emerging research on the effects of sound on the brain, as well as its potential therapeutic applications. So sit back, relax, and let’s take a journey into the wonderful world of sound!
The Physics of Sound
Before we can understand how sound travels and is processed by our brains, we need to understand some basic principles about sound. Sound is made up of tiny particles called phonons which move around in waves. These waves are caused by pressure differences between neighboring atoms or molecules. When these pressure differences are large enough, they can cause vibrations that we experience as sound.
Different frequencies have different effects on us mentally and physically because they produce different sounds. Notes that are higher in frequency (such as higher-pitched notes) travel further than notes that are lower in frequency (such as lower-pitched notes). This is because high-frequency waves move faster through air than low-frequency waves do. Additionally, higher-pitched notes carry more energy than lower-pitched notes do – which is why they tend to be louder!
How Our Ears Process Sound
Once sound reaches our ears it’s immediately converted into an electrical signal by our cochlea cells. This electrical signal then travels along nerve fibers to the auditory cortex where it’s processed into information that we can hear. The process of converting sound into information happens very quickly – within about 0.25 seconds after noise enters our ears! This quick response time helps us to identify specific sounds quickly so that we can respond appropriately (for example, when someone whispers you know what they’re saying!).
The Anatomy of the Auditory Senses
Now that we know how sound travels and is processed by the brain, we can begin to explore the psychological and neurological impacts of sound on our brains. This is the site of the acoustic technology used to create special effects in the devices that we use every day. The psychological and neurological impacts of sound can be much more complex than what we have covered here. But for now, we will just highlight a preferred application of sound therapy in applications.
What Makes Music Sound Different
Music is an amazing form of communication that has the ability to move people to tears or make them dance in joy. It’s a universal language that we all understand, and it’s thanks to music that we can share our emotions with others. While many people think of sound simply in terms of how it makes us feel, there is much more to music than that. In this section, we’ll take a look at some of the key aspects of music sound and how they impact the way that we hear it.
First and foremost, sound is fundamentally about pitch. When one note sounds higher than another, it changes the sound of the entire piece. This is why some pieces of music can seem very similar in tone but still be different due to the changes in pitch. Pitch also affects how loud a note sounds as well as how long it lasts.
Next, frequency plays an important role in how we perceive sound. High-frequency sounds are often perceived as being clearer and brighter than low-frequency sounds. This is because high-frequency sounds travel further and are less impacted by obstacles on their way to your ears.
Amplitude also plays an important role in sound – louder sounds are usually more noticeable than softer ones. This is why you’ll often hear louder instruments (like guitars or drums) before quieter ones (like pianos or flutes). And finally, overtones play a significant role in shaping the harmonic content of a note or melody. By understanding these three factors – pitch, frequency, and amplitude – you can begin to understand why certain songs or melodies sound different from others!
Read Also: The Role of Music in Film and TV
In addition, stereo recordings add depth and dimensionality to music by creating two separate duplicate copies of each audio track. This allows you to create a sense of space around each instrument while allowing for richer harmonic content due to the addition of overtones (the combination of two frequencies). And lastly, digital audio processing techniques allow for enhanced fidelity and increased dynamic range when compared with traditional analog audio recording methods.. All told, learning about music technology has tremendous implications for our understanding and appreciation of musical artistry.. so let’s dive right into it!
The Impact Of Sound On Us Humans
Sound is an important part of our lives, and its impact on us is evident in everything from our emotions to our productivity. In this section, we will discuss the different ways sound works and the effects it has on our bodies. We’ll also look at how music can have a powerful impact on our moods and how sound can be used to promote healing. We’ll also explore the ways that technology is making it easier for us to access sound and benefit from its therapeutic properties. Finally, we’ll discuss how our environment can be affected by sound pollution and what you can do to help reduce it.
How Sound Works.
When we listen to music, or any other form of sound, it travels through the air and into our ears. Our ears are specially adapted to receive and process sound waves in order to create aural experiences. Sound waves travel through the air in all directions at the same time, which makes them difficult for us to hear individually. Instead, we perceive sounds as a combination of several waves that are overlaid one on top of another. This process is known as stereo hearing.
The Effects of Different Sound Frequencies on Our Bodies.
Different frequencies have different effects on our bodies. For example, frequencies that are high in pitch tend to cause stress. Low-frequency sounds, such as those that occur during relaxation exercises or gentle rainfall, have been shown to have positive effects on mental well-being. Additionally, certain sounds are known to have healing properties – for instance, tones that produce gamma brainwaves have been shown to improve memory recall.
The Power of Music To Uplift Our Moods And Help People Heal
Music has been proven time and again as one of the most powerful tools humans have when it comes to improving their emotional states and healing wounds. Studies show that listening to music has a positive effect on both depression symptoms and anxiety levels. In fact, some doctors even recommend playing music during surgery! It’s clear then why music is such an integral part of so many cultures – its power simply cannot be understated!
All In All
Sound is more than just music; it is a powerful tool that has the power to evoke emotion, influence productivity, and even affect our physical health. We now have a better understanding of the science and mechanics behind sound, thanks to this blog post. We know how sound waves travel, how our ears process them, and what makes music sound different. We also explored the potential therapeutic applications of sound for improving mental health. Finally, we discussed some ways to reduce noise pollution in our lives.



