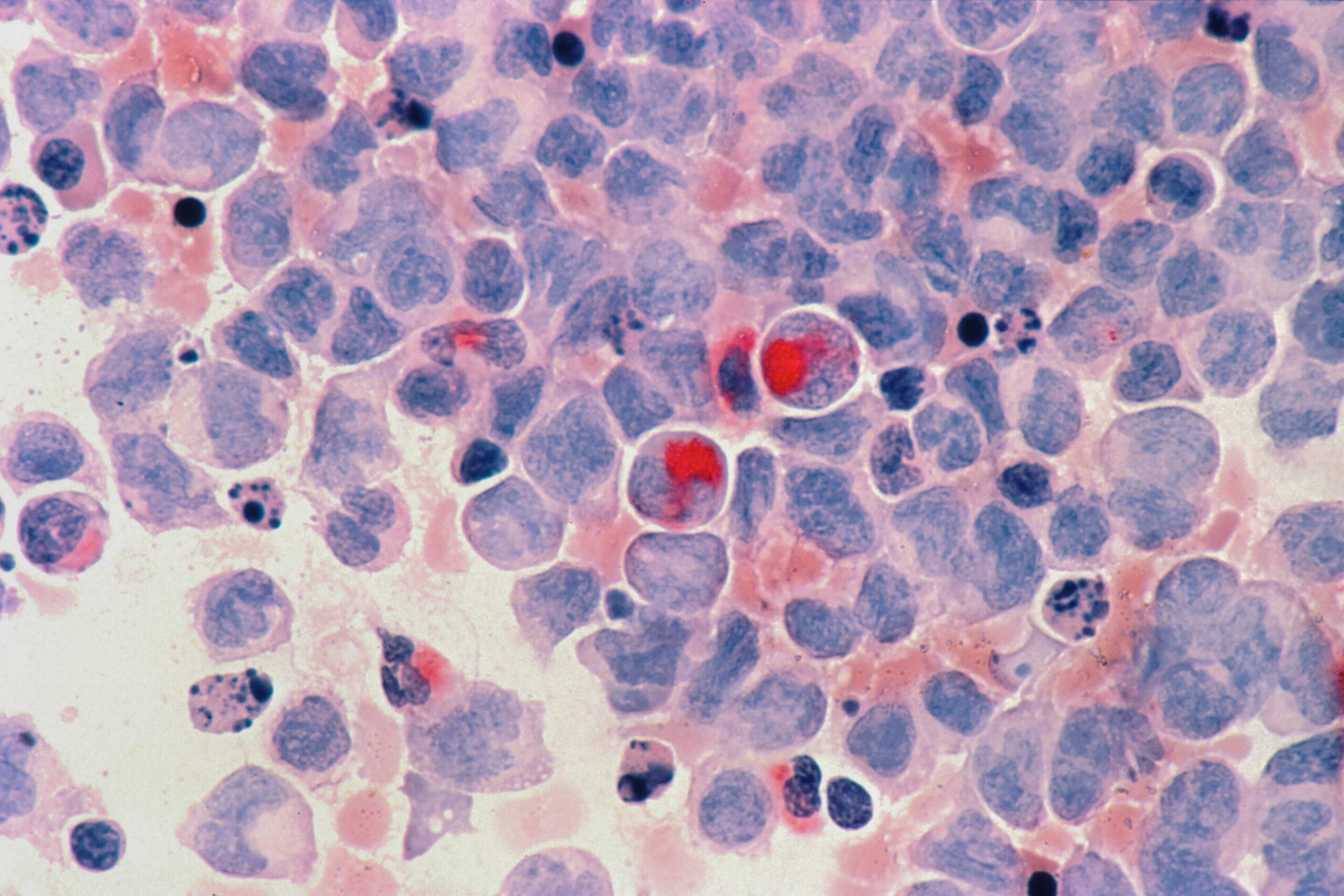
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, leading to abnormal production of immature white blood cells. It is a serious and life-threatening disease that can progress rapidly if left untreated. AML is a relatively rare disease, but it affects people of all ages and can have a significant impact on patients and their families.
In this article, we will explore the basics of AML, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, subtypes, and treatment options. We will also discuss the impact of AML on quality of life and survivorship, as well as strategies for prevention and early detection.
AML Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of AML is unknown, but certain risk factors have been identified:
- Exposure to high doses of radiation or certain chemicals has been linked to an increased risk of developing AML.
- A history of chemotherapy or radiation therapy for another cancer can also increase the risk of AML.
- Certain genetic mutations, such as the FLT3 mutation, can also increase the risk of AML.
- Other blood disorders, such as myelodysplastic syndrome, can also increase the risk of AML.
- AML can affect people of all ages, but it is more common in older adults. The risk of developing AML increases with age.
- Other factors that may increase the risk of AML include male gender, smoking, and a family history of leukemia.
How Doctors Identify and Classify the Disease?
Here are some key points to understand about how doctors identify and classify AML:
- AML is diagnosed through a combination of tests, including blood tests, bone marrow biopsy, and imaging studies.
- Blood tests can detect abnormal white blood cells and other signs of AML in the blood.
- The bone marrow biopsy is the most definitive test for AML diagnosis, as it allows doctors to examine the bone marrow cells and identify the abnormal white blood cells.
- AML is classified into subtypes based on the specific type of white blood cell affected and other factors. This information is used to determine the best course of treatment and to predict outcomes.
- The WHO classification system is commonly used to classify AML subtypes based on genetic abnormalities and other factors.
- The FAB (French-American-British) classification system is another classification system that is based on the appearance of the leukemia cells under a microscope.
Note: Common subtypes of AML include M1-M7, acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), and myelomonocytic leukemia (M4). The specific subtype of AML affects the course of the disease and the choice of treatment.
Predicting the Course of the Disease and Treatment Outcomes
AML is an aggressive disease, and the course of the disease can vary widely depending on the subtype and other factors. Prognostic factors are used to predict the likelihood of treatment success and overall survival. These factors can include age, overall health, subtype of AML, and the presence of certain genetic mutations.
The presence of specific genetic mutations, such as the FLT3 mutation, can indicate a poorer prognosis and may require more aggressive treatment. The response to initial treatment can also be used to predict treatment outcomes. Patients who achieve complete remission after initial treatment have a better chance of long-term survival.
Follow-up testing and monitoring is important to detect any signs of relapse or disease progression. This may include regular blood tests and bone marrow biopsies. Treatment for AML typically involves chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and/or stem cell transplant. The specific treatment plan will depend on the subtype of AML and other factors.
Advances in precision medicine and targeted therapies are also showing promise in treating AML, particularly in patients with specific genetic mutations. The goal of treatment for AML is to achieve complete remission and prevent relapse. Some patients may require ongoing treatment or monitoring to manage any residual disease.
AML Treatment in India
AML treatment in India is similar to the standard of care in other countries and typically involves chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and stem cell transplant. Many hospitals in India have specialized hematology and oncology departments that provide AML treatment.
The AML treatment cost in India can be significantly lower than in other countries, making it an attractive option for international patients seeking affordable care.
Several hospitals in India are accredited by international organizations, such as the Joint Commission International (JCI) and the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Providers (NABH), which ensures high-quality care.
Patients seeking AML treatment in India should research hospitals and doctors carefully and seek recommendations from trusted sources. It is important to ensure that the hospital and doctors have experience in treating AML and have access to the latest treatment options and technologies.
Patients may consider medical tourism companies like Lyfboat that specialize in arranging medical travel to India and ensure a smooth experience.
Conclusion
AML is a complex disease that can have a significant impact on those affected. Understanding the causes, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options for AML is important for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals alike. While AML is an aggressive disease, advances in treatment options and targeted therapies are improving outcomes for many patients.
AML treatment in India is a viable option for those seeking high-quality care at a lower cost. Although as with any medical decision, it is important to research treatment options and providers carefully and make informed decisions.
Read Next: What is mean by Epilepsy?